Table of Contents
Occasionally, body tissues, called biopsies, have to be extracted for detailed medical examination. Ways of achieving this in a breast include:
- Fine needle aspiration.
- core needle biopsy.
- Surgical biopsy.
What we’ll be looking at here is breast biopsy with excision which is a type of surgical biopsy. Research published in the Journal of Clinical Nursing (JCN) has shown women appointed for excisional biopsies have significant fears about what their fate would be. I hope to address some of those concerns here.1
Types of surgical breast biopsy.
Surgical biopsies are also called open biopsies and they are of two types:
1. Incisional biopsy: this aims to extract a small part of an abnormality in the breast and it’s expedient when the suspicious finding is relatively large. It reduces the negative cosmetic effect of the surgery on the breast.
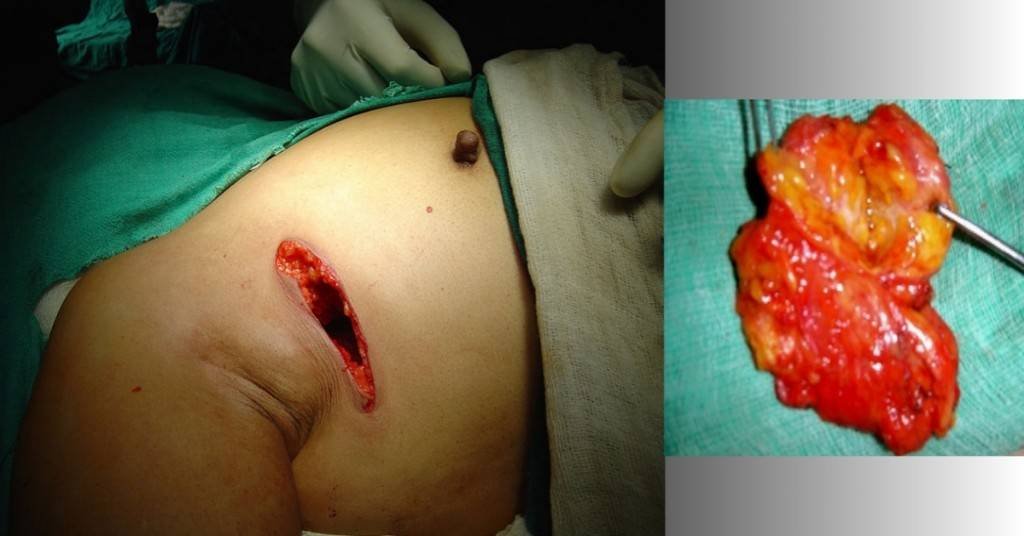
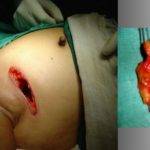
2. Excisional biopsy: The process aims to remove all of the abnormal findings in the breast and a small rim of normal healthy tissue is usually taken out with it. The process takes about 60 minutes.
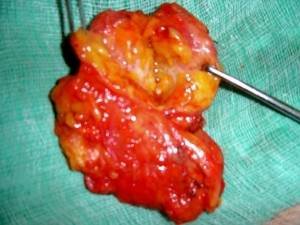
Image by Chintamani et al
If a lump for which you have to be cut open isn’t so big, wisdom demands the entire thing is removed to spare you the need for another surgery should the biopsy result reveal malignancy(cancerous lump).
Indications for breast biopsy with excision.
Though an entire lump does get removed, an excisional biopsy is essentially a diagnostic procedure meant to check for the presence of breast cancer.
The most preferred method for biopsy is the core needle biopsy, however, an excisional surgical biopsy is necessary for the following situations:
1. Failure of core needle biopsy: when the result obtained from the core needle biopsy is inconclusive.
2. Difficulty in obtaining tissue samples: When other biopsy measures couldn’t be used to obtain samples for analysis, excisional biopsy becomes the next level plan.
3. Patient preference: If you demand an outright removal of the abnormal findings your wish will usually be granted.
Apart from the above-listed scenarios, other biopsy methods are considered first for several reasons. Among the two types of surgical biopsies, excisional biopsy is often preferred to incisional.
Preparation for breast biopsy:
Days before your surgery you’ll get to meet the surgical team in an interactive session. You’ll be privileged to ask whatever questions you may have about the planned surgery. This will help allay your fears and boost your confidence.
You’ll also get to sign the consent form. Ensure to inform them of any underlying health conditions you have and raise any concerns bothering you. Important things you should bring to their notice are:
1. Diabetes: This could be a deciding factor in the type of anesthesia given. General anesthesia may require you not to take food for up to 6 hours before your surgery but a local one won’t have this protocol.
2. Medications: You must tell if you are on any medications like blood thinners that’ll interfere with normal blood clotting.
3. Haemophilia (Blood clotting disorder): This is a condition where your blood’s clotting ability after an injury is substantially weak such that you experience excessive bleeding from even small cuts or injuries.
Being hemophilic is certainly something you must bring to their notice as the surgery for a hemophilic will require additional guidelines as suggested in the official guide of the World Federation of Hemophilia.2
4. Allergic Reactions: Inform them of any allergies you may have including reactions to any of the substances or objects that’ll be used in your surgery.
Preoperative needle localization of tumor.
With the detection of impalpable (tumors that can’t be felt by touch) abnormalities in the breast, performing biopsies on them could be very impracticable and highly inaccurate. This problem is solved by preoperative localization.
Localization Procedure.
Firstly, the area is numbed with local anesthesia. Then, the overlying skin is cleaned with an antiseptic after which a hollow needle is inserted into the breast till it gets to the tumor.
This is carried out with the help of ultrasound imaging or mammogram.
With the tip of the needle in the tumor, a marker is put in place, depending on the localization type in use. Wire localization is the most common.
Localization Methods.
Localizations are not done simultaneously with the excision. Therefore, something like a wire, for instance, has to be put in place to guide the surgeon to the tumor during the excision.
Wire localization and the risks.
This is the most common method and involves the insertion of very thin, flexible wire into the breast.
At the point the hollow needle inserted into the breast reaches the tumor, a thin, hooked wire is inserted into the breast through the needle such that the hooked end secures its attachment to the tumor.
The free end of the wire, sticking out from the breast is taped to the chest after the removal of the needle. The wire serves to guide the surgeon to the location of the tumor to be excised.
As helpful as it may be, wire localization has its risks such as infections, wire migrations, inaccurate localization, and discomfort.
Other localization methods.
These are promising new methods that could replace wire localization. They include:
- Radioactive seed localization as contained in the American Journal of Surgery.3
- Magnetic seed localization as contained in the PLOS ONE journal.4
- Non-radioactive radar localization as contained in the Breast Cancer Research and Treatment Journal.5
You’ll find more details of these methods in the National Library of Medicine (NLM).6
Breast biopsy with excision.
Just as it is in mammogram screening or diagnostics, you are advised not to use deodorants, powder, and perfumes on or around your breast on the day of your surgery.
Image credit: PxHere
Procedure
Image by آرمین
1. You’ll be given anesthesia intravenously (through your veins). This will be given time to work before the commencement of your surgery. If general anesthesia is used, your vital signs (blood pressure, respiratory rate, oxygen level, etc.) will have to be monitored during your surgery.
2. The overlying skin is cleaned with a sterile solution.
3. The surgeon then makes a small cut on the skin and breast tissues using the wire previously used in the wire localization of the tumor, as a guide. The wire is taken out with the excised tissue.
4. In an excisional biopsy, all of the tumors have to be removed and taken to the lab for investigation. This is where it differs from the incisional biopsy. Usually, a rim of normal breast tissue surrounding the tumor will be removed with it.
5. The excised tissue may be x-rayed to ensure the right tissue was removed as detected in your mammogram. A second attempt may be done if the excised area doesn’t match what was shown in your mammogram.
6. A small marker may be placed where the lump is removed. This is to help identify the site when the need arises.
7. The cut made through the breast is finally closed up with stitches and appropriate dressing.
Risks
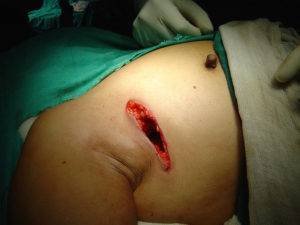
Image credit: Chintamani et al
This is usually a safe procedure but just as there is a level of risk in almost all surgical operations, breast biopsy with excision isn’t left out. Possible risks include:
- Infection: It’s more prone to be infected than other methods since it’s more invasive.
- Bleeding and swelling: These are rare occurrences but do happen.
- Altered breast shape: The shape of your breast may change depending on the size of the tissue removed.
- Surgical scar. This is usually small.
- Failed excision: In very rare cases the tumor may not have been properly removed which may call for another surgery.
Your results.
Firstly, your impalpable tumor localization is carried out by a doctor called a radiologist, and then another doctor (a surgeon) does the breast biopsy with excision.
This time a third doctor called a pathologist is responsible for analyzing the sample under a microscope to see if there are cancer cells.
More often than not, there won’t be cancerous cells and you’ll be informed when to resume your normal mammogram.
If it turns out the tumor is cancerous, he checks for the characteristics and to see if the rim of normal tissue excised with it suggests adequate removal of the cancerous cells. This information and further tests that could be done will help to plan your treatment.
It could take up to 2 weeks to get your result.
Excisional breast biopsy vs. core needle biopsy.
Breast biopsy with excision is great in tackling the menace of cancer but there are reasons why core needle biopsy is preferable as contained in the Journal of European Radiology. Let’s have a look at how they stack up against each other in the table below.7
| Breast biopsy by excision. | Core needle biopsy. |
|---|---|
| May alter the shape of your breast. | Intact breast shape. |
| Higher chances of infection. | Reduced chance of infection. |
| Scarring. | Usually no scarring. |
| You may end up with more than one surgery. | One surgery is usually required and that happens if cancer is detected. |
| Costlier. | Cheaper. |
| Riskier. | Less risky. |
| You may have had an avoidable surgery. | Most times you end up with no surgery at all. |
My last point reiterates the fact that most biopsies end up finding no cancer. Having a breast biopsy by excision may mean having a surgery that could have been avoided with all the risks that go with it.
A core needle biopsy may result in an underestimation of the scope of a disease in some cases. Click To TweetRecovery time after biopsy.
Cryotherapy could be beneficial in the first 2 to 3 days to reduce the pain or discomfort. In the absence of infections, healing should take place within 2 weeks post-op (that’s 2 weeks after the operation). Unusual pain beyond recovery timing should be reported to your doctor.
Most times when my patients have unnecessary pain beyond reasonable time post-op, it may be due to an infection but this isn’t common. Infections also delay healing and recovery so it needs to be given prompt attention so it doesn’t get worse or even spread, resulting in septicemia.
Swelling, post-op may take up to 8 weeks or less to clear before which you should have long returned to your daily routine. However, within the first 2 weeks post-op, it’s wise to avoid physical activities that put pressure on the chest area, especially the breasts.
Walk as much as you can but don’t jog or go running. Generally, avoid things that get the breasts bouncing merrily as women do but rather wear a supportive bra.
Finally, all is well that ends well. The good thing is it usually ends well even if you are among the class of women that seldom adhere to instructions. The pain will check all excesses till healing is complete.
After all, everyone is afraid of pain which is a reason some shy away from life-saving mammograms.
You may also want to get some insight about mammograms of breast cancer and those abnormalities that could lead to breast biopsies with excision.
References.
- Demir, F., Donmez, Y. C., Ozsaker, E., & Diramali, A. (2008). Patients’ lived experiences of excisional breast biopsy: A phenomenological study1. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 17(6), 744-751. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2007.02116.x ↩︎
- RICKARD, K. A. (1994). Guidelines for therapy and optimal dosages of coagulation factors for treatment of bleeding and surgery in hemophilia. Haemophilia, 1(S1), 8-13. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2516.1995.tb00104.x ↩︎
- Gray, R. J., Pockaj, B. A., Karstaedt, P. J., & Roarke, M. C. (2004). Radioactive seed localization of nonpalpable breast lesions is better than wire localization. The American Journal of Surgery, 188(4), 377-380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2004.06.023 ↩︎
- Lindenberg, M., & Retèl, V. (2020). Early budget impact analysis on magnetic seed localization for non-palpable breast cancer surgery. PLOS ONE, 15(5), e0232690. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0232690 ↩︎
- Lee, M.K., Sanaiha, Y., Kusske, A.M., et al. A comparison of two non-radioactive alternatives to wire for the localization of non-palpable breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat 182, 299–303 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-020-05707-1 ↩︎
- Cheang, E., Ha, R., Thornton, C. M., & Mango, V. L. (2018). Innovations in image-guided preoperative breast lesion localization. The British Journal of Radiology, 91(1085). https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20170740 ↩︎
- Schueller, G., Schueller-Weidekamm, C. & Helbich, T.H. Accuracy of ultrasound-guided, large-core needle breast biopsy. Eur Radiol 18, 1761–1773 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-0955-4 ↩︎






























































































Hello! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to give a
quick shout-out and say I really enjoy reading through your blog posts.
Can you suggest any other blogs/websites/forums that go over the same subjects?
Thanks!
I’m so glad to hear from you, more so, that you enjoy reading my posts. That’s super encouraging and thanks for that. In my nearly 20 years of clinical practice, I’ve enjoyed spending time with my patients listening to them, and educating them about the conditions they present with.
There are several trustworthy sites that discuss the same topics and a few of them are:
cancer.org by American cancer society, Cancerresearchuk.org, Clevelandclinic.org, mayoclinic.org, etc.