Table of Contents
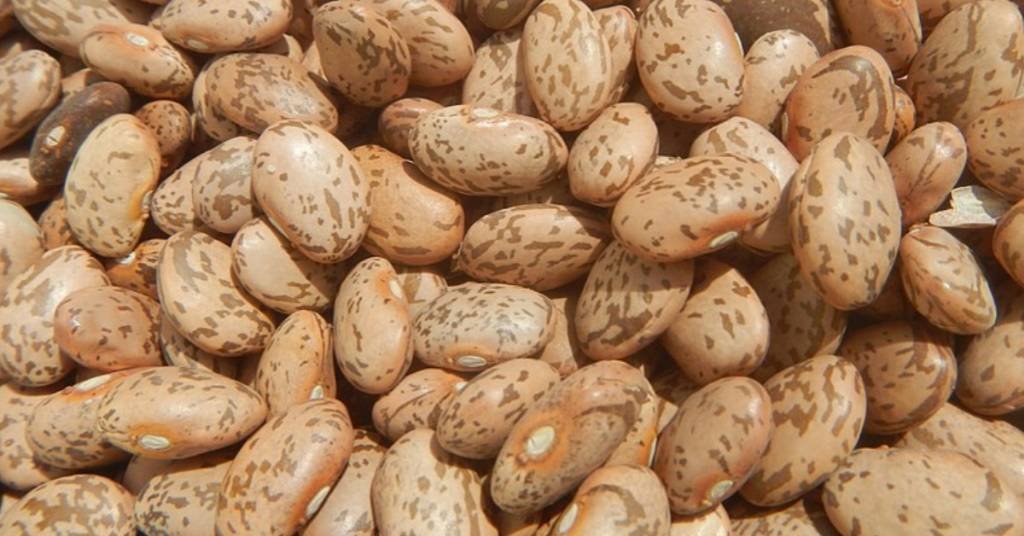
Pinto beans are beige-colored and oval-shaped with reddish-brown spots making each look like a piece of painting. One cup of beans boiled with salt contains 245kcal of energy, 15.4g of protein, 1.11g of total lipids, 15.4g of dietary fiber, 78.7mg of calcium, 746mg of folate, and 3.57mg of iron.
They are popular in Southern parts of the US and are known for their creamy, earthy, and nutty flavor. They are eaten whole or mashed. You may buy them as canned or dried beans in the stores though canned ones may contain sugars and salts.
In this article, we’ll focus on proven1 The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. (scholarly source) visit source nutrition facts for pinto beans, the health benefits2 Critical reviews in food science and nutrition. (scholarly source) visit source it offers and the downsides of eating the beans.
Nutrition facts for 1 cup of pinto beans boiled with salt
A cup of pinto beans weighs about 171g. When boiled it could rise up to three times its initial size. Below are the Pinto bean nutrition data for a boiled cup of pinto beans with salt according to the US Dept of Agriculture.3United States Dept. of Agriculture. (governmental authority) visit source
|
Nutrient facts for 1 cup of pinto beans boiled with salt. |
||
|
Nutrient |
Amount |
Percentage of the daily value |
|
Water |
108g |
– |
|
Energy |
245kcal |
12% |
|
Protein |
15.4g |
31% |
|
Total lipid(fat) |
1.11g |
1% |
|
Ash |
2g |
% |
|
Carbohydrate |
44.8g |
16% |
|
Total Dietary fiber |
15.4g |
55% |
|
Sugars(sucrose) |
0.581g |
1% |
|
Starch |
26g |
% |
|
Calcium |
78.7mg |
6% |
|
Iron |
3.57mg |
20% |
|
Magnesium |
85.5mg |
29% |
|
Phosphorus |
251mg |
20% |
|
Potassium |
746mg |
16% |
|
Sodium |
407mg |
18% |
|
Zinc |
1.68mg |
15% |
|
Copper |
0.374mg |
42% |
|
Manganese |
0.775mg |
34% |
|
Selenium |
10.6µg |
19% |
|
Vitamin C |
1.37mg |
2% |
|
Thiamine |
0.33mg |
28% |
|
Riboflavin |
0.106mg |
8% |
|
Niacin |
0.544mg |
3% |
|
Pantothenic acid |
0.359mg |
7% |
|
Vitamin B-6 |
0.392mg |
23% |
|
Folate |
294µg |
74% |
|
Vitamin E |
1.61mg |
11% |
|
Vitamin k(phylloquinone) |
5.98µg |
5% |
|
Total saturated fatty acids |
0.186g |
1% |
|
Saturated fatty acids 16:0 |
0.181g |
– |
|
Saturated fatty acids 18:0 |
0.003g |
– |
|
Monounsaturated fatty acids 18.1 |
0.181g |
– |
|
Total polyunsaturated fatty acids |
0.321g |
– |
|
Polyunsaturated fatty acids 18:2 |
0.133g |
– |
|
Polyunsaturated fatty acids 18:3 |
0.186g |
– |
|
Source: The US dept of Agriculture |
||
Proteins: Proteins are body-building foods and pinto beans are substantially rich in them. A serving of 171g of boiled pinto beans gives you as much as 15g of protein. This represents 31% of your daily value.
It’s a very reliable source of protein for vegetarians, however, it doesn’t contain all the essential amino acids needed in your body and therefore isn’t a complete protein. That means if you are a vegetarian you have to eat other sources of plant-based proteins like nuts to get a complete protein.
Essential amino acids are those that the body can’t produce by itself so you have to rely on your diet for them.
Carbohydrates: Carbs provide you with the energy needed in your activities of daily living. Pinto beans are good sources of carbohydrates with less impact on blood sugar. This makes them ideal for diabetics as well as everyone else.
Fats: Pinto beans are low in fat so are a great source of nutrition without the risks associated with high-fat diets. A whole cup has only about 1% of your daily value for fats. Canned pinto beans may have higher amounts of fat content as they may be processed with added fats.
Vitamins: Vitamins are an indispensable part of a balanced diet. A cup of Pinto beans provides you with daily values of as much as 74% of folate, 23% of Vitamin B6, and 28% of thiamine, among several others.
Minerals: It is very rich in minerals such as iron, magnesium, sodium, manganese, copper, calcium, etc., all of which play vital roles in health maintenance and numerous other physiological processes in your body.
Keep in touch by signing up for our newsletter.
Nutrition facts for 1 cup of boiled pinto beans without salt
For a cup of pinto beans boiled without salt, the nutrient composition remains exactly the same as we have in the table above except for sodium. So there will be no need to reproduce the entire table just to alter the amount of sodium alone.
The normal table salt is sodium chloride (NaCl) which contains sodium and chlorine as salt.
The amount of these two elements present in the cooked beans will depend on the amount of added salt. So where no salt was added, we’ll have only an amount of sodium occurring naturally in the beans. This is found to be 1.71mg. A figure that represents just about 0.0007% of the daily value.
It also has 60.4mg of Choline and 0.171mg of Betaine.4 The US dept. of Agriculture. (governmental authority) visit source

Image credit: Flickr
Nutrition Facts for pinto beans chili
Pinto bean chili is made from dried pinto beans cooked with chili powder and a couple of other ingredients depending on the preferences of the cook. Pinto bean nutrition data for a serving size of 130g.
|
Nutrition facts for pinto bean chili: Serving size – 130g |
||
|
Nutrient |
Amount |
Percentage daily value |
|
Energy |
130kcal |
7% |
|
Total fat |
1g |
1% |
|
Sodium |
471mg |
20% |
|
Total Carbohydrate |
22g |
8% |
|
Dietary fiber |
8.1g |
29% |
|
Sugar |
1g |
– |
|
Protein |
7g |
14% |
|
Calcium |
40mg |
3% |
|
Iron |
1.9mg |
11% |
|
Potassium |
380mg |
8% |
|
Source: Nutritionvalue. |
||
The percentage daily values are based on a 2,000-calorie diet.
Nutrition Facts for Cracker Barrel Pinto Beans
Pinto bean nutrition data for cracker-barrel is as follows:
|
Nutrition facts for 1 serving size of cracker barrel pinto beans. |
||
|
Nutrient |
Amount |
Percentage daily value |
|
Energy |
140kcal |
7% |
|
Total fat |
2g |
3% |
|
Saturated fat |
1g |
5% |
|
Cholesterol |
15mg |
5% |
|
Sodium |
260mg |
11% |
|
Total Carbohydrates |
21g |
8% |
|
Dietary Fiber |
7g |
25% |
|
Protein |
10g |
2% |
|
Source: Nutritionix |
||
The percentage daily values are based on a 2,000-calorie diet.
Nutrition Facts for canned pinto beans
This is one of the forms in which pinto beans are sold. The following are the nutrients you can expect from a serving size can of 442g and the percentage of the daily value.
|
Nutrition facts for canned pinto beans of serving size can of 442g. |
||
|
Nutrient |
Amount |
Percentage daily value |
|
Energy |
362g |
18% |
|
Total fat |
2.5g |
3% |
|
Saturated fat |
0.5g |
3% |
|
Polyunsaturated fat |
0.9g |
|
|
Monounsaturated fat |
0.5g |
|
|
Sodium |
1185mg |
52% |
|
Potassium |
1219.9mg |
26% |
|
Total Carbohydrates |
67g |
24% |
|
Dietary fiber |
20g |
71% |
|
Sugars |
4.5g |
9% |
|
Protein |
20g |
40% |
|
Vitamin C |
5.2% |
|
|
Calcium |
208mg |
16% |
|
Iron |
6.5mg |
36% |
|
Source: Nutritionix |
||
The percentage daily values are based on a 2,000-calorie diet.

Health benefits of Pinto beans
1. Antioxidants: Antioxidants are substances that prevent damage to the body cells by free radicals and slow the aging process.5 National Library of Medicine. (governmental authority) visit source Pinto beans are rich in known antioxidants like polyphenols and flavonoids.
2. Reduced risk of heart disease: High levels of low-density lipoproteins are associated with an increased risk of heart disease.6 National Library of Medicine. (governmental authority) visit source Pinto beans have been shown to lower blood cholesterol levels including the bad cholesterol called Low-density cholesterol (LDL). This reduces your risk of developing heart disease.
3. Fiber-rich for digestive healthcare: Pinto beans are an excellent source of dietary fiber. A cup of it has over 15g of fiber which represents not less than 55% person of your total daily value. Fibers enhance digestion, and trap cholesterol, preventing your body from absorbing it.
This action reduces low-density lipoproteins and improves heart health.7 National Institute of Health. (governmental authority) visit source
4. Blood sugar management:8National Library of medicine. (governmental authority) visit source With a glycemic index of 39 pinto beans are perfectly suited for people living with diabetes. Usually, foods with a glycemic index below 55 are considered good for diabetics. It also has a fair glycemic load of 10.
With pinto beans you have reasonably reduced chances of blood sugar spikes after a meal, however, the quantity taken per meal still matters for diabetics.
5. Weight loss: The high protein and fiber content of the beans have been found to help weight loss as these food nutrients leave you feeling full. This reduces your tendency to consume more calories.9Pubmed. (governmental authority) visit source
6. Reduced cholesterol levels: The rich fiber content of pinto beans traps cholesterol thereby reducing its absorption in the intestines. In this way, it reduces your general levels of cholesterol.
7. Lowered risk of cancer: Certain antioxidants found in pinto beans like Kaempferol, and Biochanin-A is also anti-inflammatory and help in the fight against cancer.10Healthcrust article. (trustworthy) see the article 11Healthcrust article. (trustworthy) see the article
Biochanin-A is an O-methylated isoflavone that is known to induce apoptosis and reduce the proliferation of cancer cells. Click To TweetDownsides of pinto beans
1. Lack of vitamin B-12: This vitamin is essential in the formation of red blood cells, DNA, brain, and nerve cells. Unfortunately, it’s not found in the beans.
2. Allergenic: It’s a known allergenic food like other legumes or nuts. If you are allergic to these foods you may want to find out from your healthcare provider if pinto beans are right for you.
3. Bloating and gas: Pinto beans contain a type of carbohydrate called raffinose. This is left undigested and by the time it gets to the large intestine gets broken down by bacteria to form gas. This could give quite unpleasant outcomes.
4. Presence of anti-nutrients: like many other plant-based foods pinto beans also have anti-nutrients like lectins and phytic acids. When consumed in reasonable quantities they inhibit the intestinal absorption of certain nutrients.
However, this shouldn’t be seen as much of a problem as the anti-nutrient contents are reduced during cooking or preparation.
I hope this piece was informative. You may also be interested in the nutrition of peanut butter.