Table of Contents
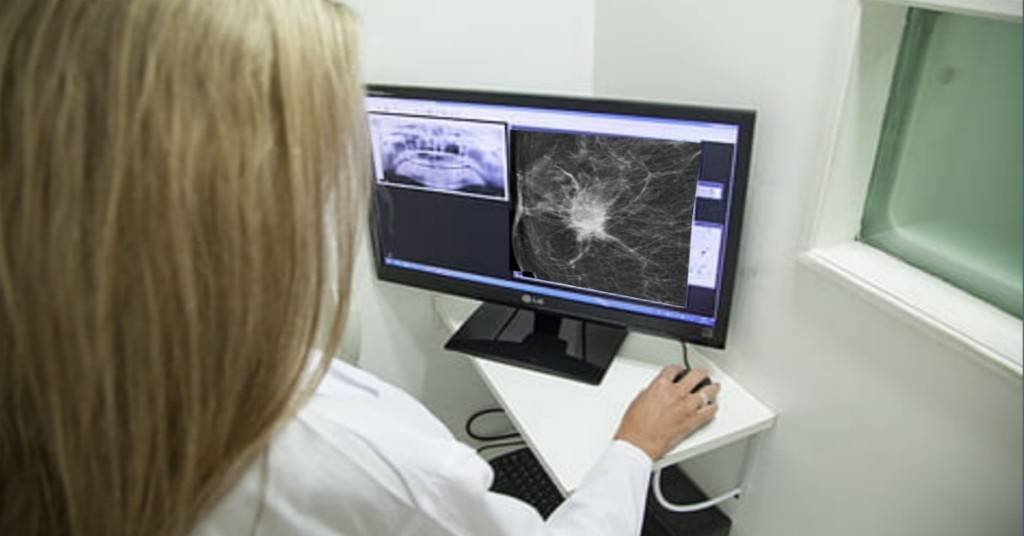
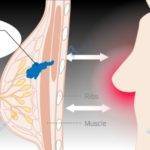
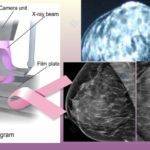
Mammogram 3D, otherwise known as digital breast tomosynthesis is a computerized 3-dimensional digital image of the breast obtained by the combination of multiple images taken from different angles by a 3-D machine.
It is an advancement in breast imaging technology over the last 10 years which has greatly improved the clinical efficiency and reliability of mammograms in the early detection of breast cancers.
3D mammogram machine.
There have been two generations of the machine
First Generation.
This was approved around 2011 by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). However, due to certain shortcomings, it wasn’t so desirable as it prolongs the stage of breast compression in addition to greater exposure to radiation.
Second generation.
They were approved by the FDA 2 years later in 2013 and were better accepted. This is because they were able to address the problems with the first-generation machines and had clear advantages like:
- Cutting off the need for extra radiation exposure for 2-D by using the same images obtained for mammogram 3D to create 2D mammograms.
- Reduces the level of compression applied on breast tissues, significantly without a reduction of image quality.
- The duration of compression, and by extension, the discomfort was also significantly shorter.
- Has about 40% improved chances of accurately detecting breast cancer.
- The recall rate is shortened by up to 15% too.
For these reasons, the 2nd generation was widely accepted and is increasingly being used in the screening and diagnosis of breast cancers.
Mammogram 3D pros and cons.
Pros.
- Has fewer false positives. That is tumors that were thought to be cancers but proved to be benign after putting you through much anxiety and the costs of extra tests.
- Reduction in the superimposition of breast tissues thereby reducing the errors that could occur in interpreting your mammograms.
- It generally gives better images when used for dense breasts than the standard 2D.
- Reduces the rate of recalls for further testing.
- Enables Radiologists to view beyond areas of breast density so are actually the best for dense breasts.
- Breast implants obscure breast tissues in mammograms. Studies have shown mammogram 3D to be the best choice if you have implants.
Cons.
- Usually costs more.
- Not covered by all insurance outfits.
- Not as widely available as the standard 2D especially in rural areas.
- Radiologists may need special training to be able to read 3D images.
- Could take more than twice as much time to read since there are much more images to view.
- It has higher capital and maintenance costs.
- It may be difficult to tell if a mass seen in 3D mammograms is solid or a cyst without calling for an ultrasound.
Guidelines for 3D mammograms.
A. Endeavor to locate a center near you that offers mammogram 3D.
B. Make sure you verify with your insurance provider if they cover 3D mammogram screening.
C. Avoid coffee and tea for a week before your appointment as caffeine can make your breasts tender and lumpy. This could increase the discomfort, you may feel during mammography.
D. If you are premenopausal, plan your test away from your cycle for a time when your breasts are least tender.
E. Go along with previous mammograms, if any.
F. Avoid deodorants, powders, perfumes, and other substances that may affect your mammogram. These substances appear as white spots in mammograms thereby mimicking abnormalities
Most of the other guidelines are generally in line with the usual guidelines for 2D mammograms so there may be no need to repeat them.
Do keep in touch by signing up for our newsletter:
Mammogram 3D procedure.
1. You’ll have to take off all jewelry, especially nipple rings if you are one of those who enjoy having them there.
2. You may be given a gown that’s a better fit for the procedure.
3. Next, you’ll stand in front of the machine for your breast to be positioned on its lower plate.
4. An upper transparent plastic plate is gently lowered to the point it compresses your breast, thereby flattening out your breast tissues for better imaging.
This is the point you may feel some discomfort or even pain but it’ll be just for a few seconds, trust me.
5. The imaging lever or arm of the mammogram 3D machine moves over your breast in an arch, taking multiple images of your breast as it does so. You’ll need to be very still at this point.
6. Your breast is released from the machine for it to be repositioned from the side for another set of images to be taken.
7. The entire process is repeated on the contralateral breast (that is, the opposite breast).
8. The series of images taken on each breast are processed by a computer which then produces 3D images of your breasts.
The 2nd generation mammogram 3D machines discussed above are also known for their ability to synthesize 2-D images from exactly the same set of images from which they produced the 3D mammogram.
This saves much time and considerably less exposure to radiation than if you were to repeat the process separately to obtain 2-D images.
Many of the mammogram 3D procedures are quite similar to the conventional mammogram procedure we discussed in an earlier article.
Mammogram 3D versus 2D.
They are very similar to what was previously discussed on how long mammograms take on account of the slightly added time expected from mammogram 3D.
| 3D mammogram | 2D mammogram |
|---|---|
| Involves multiple images, taken from multiple angles. | Involves two images taken from two angles, top and side. |
| Less false positives. | More false positives. |
| Takes a slightly longer time. | Takes a slightly shorter time. |
| Prevents superimposition of breast structures. | Structures may get superimposed. |
| More radiation exposure. | Less radiation exposure. |
| Can reveal cancers missed in 2D. | Can miss cancers detectable in 3D. |
| A Radiologist may require special training to read images. | No special training is required. |
| Gives clearer images beyond areas of breast density. | Images can be obscured by breast density. |
Though each mammogram 3D and 2D has its advantages, studies have shown combining the two is more beneficial for :
- Improving the diagnosis of breast cancers in people with implants.
- Reducing the possibilities of missing cancers.
- Reducing the need for follow-up imaging.
- Reducing the need for other modalities or machines.
- Improving the detection of cancers or other abnormalities in people with dense breasts.
Mammogram 3D cost.
The cost could vary widely across locations, types of mammograms (screening or diagnostic), insurance coverage, etc. However, the US national average for out-of-pocket costs is around $560.
Not all insurance companies cover mammogram 3D but most do, like Medicaid and Medicare. You’ll find a lot of information on the costs here.
MDsave seems to offer impressive discounts on all mammography costs with its national average at $332. With them, you are expected to save $228 but I’d love to know how true it is from your personal experiences.
I hope this article is helpful. If not, let me know how I can improve on it in addressing your questions or concerns.



























































































































I’ve been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this blog. Thanks , I’ll try and check back more often. How frequently do you update your site?