Table of Contents
There have been advancements in the neurointerventional treatment of stroke such that despite a global increase in incidence, the mortality rate has been on the decline though a study has shown there has been no change in the survival rate following hemorrhagic stroke.
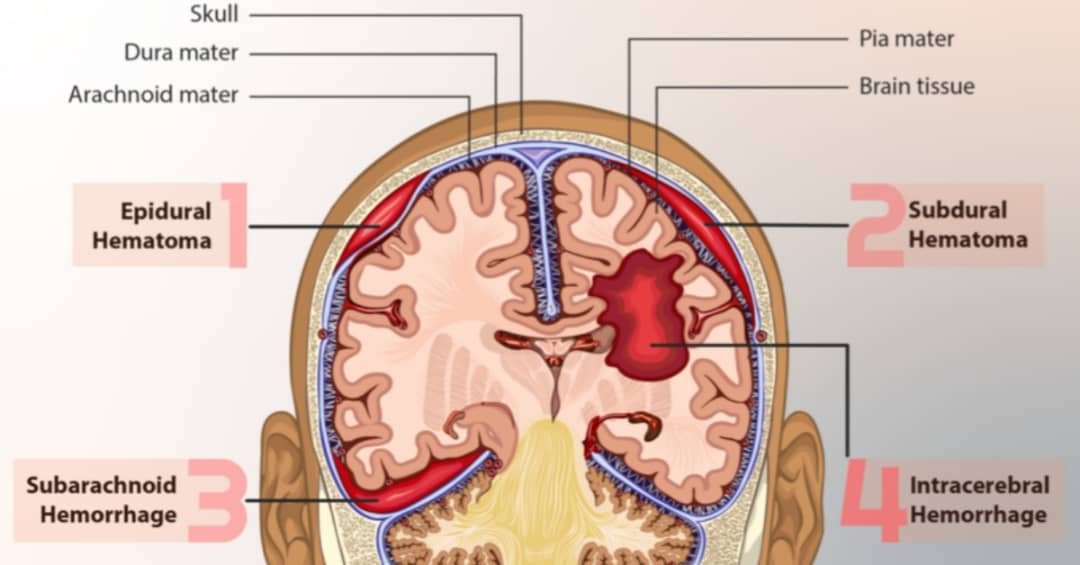
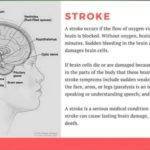
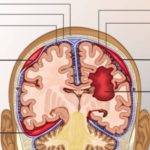
Hemorrhagic stroke is usually characterized by intracranial bleeding which could be either intracerebral or subarachnoid hemorrhage. This deprives brain cells of the oxygen and nutrients they need leading to cell death. The pressure caused by the accumulation of blood could also result in further brain damage.
Stopping the hemorrhage is a very important first-line treatment approach that may require surgery in some cases. Advances in technology and gadgets have made it possible to carry out these surgeries without the need to open up the cranium or skull.
In this article, we’ll look at the treatments for hemorrhagic stroke among other things such as the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, rehabilitation, and prevention.
Causes of hemorrhagic stroke.
Intracranial bleeding that results In hemorrhagic stroke has several causes or factors that increase your risk of having one. Some of these are:
1. Hypertension: It is responsible for the vast majority of hemorrhagic strokes. Intracerebral bleeding caused by hypertension often happens in the middle, anterior, or posterior cerebral arteries including those that originate from basilar arteries.
2. Chronic disease of the liver: This can result in the impairment of your blood’s ability to clot (coagulopathy) or low platelet count (thrombocytopenia). Both of these increase your risk of intracranial hemorrhage. (source)
3. Deposition of amyloid-β peptides in arterial walls: It results in a condition called cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) and could cause recurrent cerebral hemorrhages. The older you get the higher your risk of developing cerebral amyloid angiopathy and as much as half of the 70-year-olds have it.
4. Smoking: Cigarette smoking is an established risk of hemorrhage according to studies.
Stay in touch by signing up for our newsletter:
5. Age: As you age your risk also increases.
6. Sex: Men generally are known to be at a greater risk of having an intracranial hemorrhage.
7. Medications: Reducing the blood’s clotting ability via dual antiplatelet treatment places you at a higher risk.
8. Drugs: Sympathomimetic drugs like heroin, ephedrine, and cocaine that are known to stimulate sympathetic nerves are also important risk factors.
9. Tumors: Metastasis and other tumors like lymphoma, hemangioblastoma, and meningioma that result in bleeding could also result in cerebral hemorrhage.
10. Heavy alcoholism: Studies have shown that heavy alcoholism places you at significant risk of hemorrhage. (source)
Symptoms and complications of a stroke.
Hemorrhagic stroke, just like any other stroke, is caused by some kind of damage or death of brain cells. You do expect quite similar symptoms as seen in transient ischemic attacks or hemiplegia due to brain damage of ischemic origin. Some of these symptoms are:
- Muscle weakness or complete paralysis usually on one side of the body,
- Difficulty in standing,
- Difficulty in walking,
- Difficulty in comprehension,
- Difficulty in eating and drinking,
- Difficulty in talking(aphasia) in some people,
- Severe headache,
- Vision problems,
- Seizures,
- Facial asymmetry with deviation to the unaffected side,
- Loss of consciousness in some cases,
- Incontinence,
- Vomiting,
- Loss of cutaneous sensation in some people.
Most people will only experience some of these symptoms which may later be accompanied by some complications such as:
- Muscle atrophy,
- Spasticity,
- Bed or pressure sores,
- Soft tissue contractures,
- Joint stiffness,
- Urinary tract infection from the use of catheters.
While some of these complications can be prevented, others can be managed or kept at minimal levels with a good and continuous physical therapy or rehabilitation program.
Spasticity, which is the main reason for deformities, could go away in a few years or remain for the rest of one’s life.
Diagnosis.
The importance of accurate and timely diagnosis can not be over-emphasized. It goes a long way in determining both the treatment to be administered and the treatment outcome in the short and long terms. Tests that could be conducted include the following:
Physical checkup: The first thing one could tell from a physical examination is what side of the brain was affected. Weakness on the left side of the body indicates injury to the right side of the brain. Through physical exams, your doctor can also tell the extent of the paralysis or weakness among other things.
Your blood pressure at the time and other vitals are also checked.
Magnetic resonance Imaging: It involves the use of a machine that creates images of the brain using strong magnetic fields and radio waves.
Computerized tomography scan: This involves the use of a series of X-rays taken at different angles to create cross-sectional images of your brain. This is useful in the determination of the type of stroke you had.
Blood tests: Evaluating the Clotting factors of your blood, blood sugar levels, etc., are also parts of routine checks.
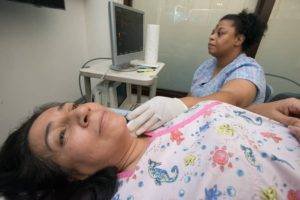
Carotid ultrasound: The carotid artery is an important section known for the accumulation of plaques that result in strokes. An ultrasound reveals the situation and what medications you may need. Though this may not diagnose a hemorrhagic stroke, it can be taken as an important test for the prevention of another stroke.
Echocardiogram: This is the use of sound waves to check how the heart works and its state of health.
Electrocardiogram: It’s used to check for the heart’s electrical activities and rhythm.
The treatment team for hemorrhagic stroke.
Though you may spend far more time with a physical therapist in an often long-term treatment program, hemorrhagic stroke treatment is a multi-disciplinary one. Several healthcare professionals will be involved in your treatment. They may include:
- Neurologist/neurosurgeon,
- Cardiologist,
- Physiotherapist,
- Occupational therapist,
- Physiatrist,
- Nurses,
- Speech therapist,
- Dietitian,
- Psychologist,
- Case manager, etc.
You will usually start with the neurologist and cardiologist who orders or conducts relevant examinations. Physical therapy or rehabilitation programs are usually started after a diagnosis has been made and you have been stabilized. However, the goal should be to commence physical therapy as soon as possible.
Though you’ll spend far more time under the care of a physical therapist, all healthcare professionals involved in your treatment are equally important. There will be variations in the type of healthcare providers needed for each patient. For instance, speech therapists may only be involved if your speech is affected.
Standard treatments for hemorrhagic stroke.
Though the incidence of hemorrhagic stroke has been on the rise, there has also been advancement in neurointerventional treatments with better outcomes such that surgeries can now be done without opening the skull. This operation is usually aimed at stopping the bleeding or reducing the intracranial pressure that results from the hemorrhage.
Other forms of intervention are the use of nasogastric tubes, delivery of oxygen through nasal tubes or facemasks, and compression stockings for prevention of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), etc. ( source)
The type of treatment can be broadly divided into emergency or medical interventions and rehabilitation.
Emergency or medical treatment.
The fatality rate after intracranial hemorrhage depends a lot on how efficient critical care or early intervention is. (source)
The focus of emergency treatment is stabilizing the patient, stopping the intracranial hemorrhage, and preventing further brain damage due to any possible increase in intracranial pressure. This may involve surgical interventions but it’s often not needed since the rupture is often found to be minimal with small bleeding.
It is common for a hemorrhagic stroke patient to be also diabetic. Achieving both blood sugar and blood pressure control is part of an ideal medical intervention.
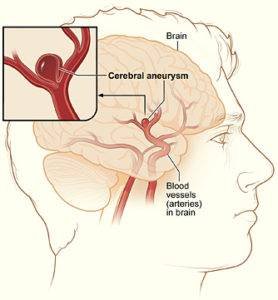
Where surgery is indicated, the type of surgery will depend on the cause of the bleeding and the extent of the rupture. Possible surgical procedures include:
1. Coiling: This could be by either endovascular coiling or stent-assisted. (source)
- Endovascular coiling: It’s a minimally invasive procedure during which a catheter is passed from the groin to the vessel in the brain where the aneurysm is located. Platinum coils are then released at the site which initiates clotting that shuts off blood from reaching the aneurysm.
- Stent-assisted coiling(SAC): This is another minimally invasive procedure meant to tackle larger aneurysms. A coil is placed in the aneurysm and a wire-mesh tube is used to cover up the mouth or opening leading into the aneurysm.
2. Clipping of an aneurysm: A small metal clip is placed at the neck of the aneurysm to seal it off so blood no longer flows to it.
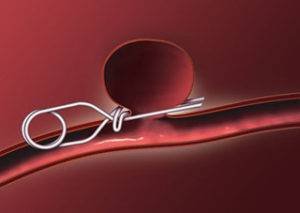
3. Endovascular embolization: It’s another minimally invasive surgery meant to seal an arteriovenous malformation using glue, balloon, foam, etc., via a catheter. When metal coils are used rather than the listed items, it is called coil embolization. (source)
4. Gamma knife radiosurgery: This is a type of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) used to treat arteriovenous malformations in the brain. Unlike traditional surgery, no incisions are made. The radiation results in scaring and shrinking of the abnormal areas thereby reducing the possibility of bleeding.
5. AVM removal by open surgery: Where possible, this procedure is done to remove the arteriovenous malformation, and redirection of blood to flow through the normal vessels.
6. Decompression craniectomy: This surgical procedure is performed to relieve pressure from the brain tissues as a result of the hemorrhage. This prevents further brain damage as a result of the pressure.
Rehabilitation.

Rehabilitation to regain lost function and independent living is also a very important intervention and will usually require the direct involvement of all or some of the following professionals: (source)
- Physical therapist. (source)
- Occupational therapist,
- Speech therapist.
Recovery is a process that could take a couple of months or years. The first 4-12 weeks post-stroke is usually the time of fast recovery and patients that could gain full functional recovery usually achieve that within this time. The rehabilitation program has to be intensive but tolerable to the patients.
Where full functional restoration isn’t possible a long-term plan could be put in place to combat the complications that may arise from residual paralyzes such as limb deformities and atrophy. Rehabilitation following a hemorrhagic stroke is similar to that for ischemic stroke or hemiplegia in general.
Some survivors are unable to eat adequate amounts of food which can interfere with recovery and increase the risk of residual paralysis or impairment. This has to be addressed possibly even before discharge from the hospital.
Life expectancy after a hemorrhagic stroke.
Stroke is known to have a huge impact on the life expectancy of its survivors such that the 5-year survival rate for hemorrhagic stroke is about 26.7%. (source ) This figure is much better for younger patients who are not diabetic, hypertensive, or alcoholic.
Age and severity of impairment are believed to be determinants of life expectancy. However, studies have shown that stroke patients with perimesencephalic hemorrhage have a normal life expectancy. (source) The table below shows the survival probabilities for hemorrhagic stroke patients from 6 months to 3 years after stroke.
| Time | Probability of survival |
|---|---|
| 6 months. | 36% |
| 1 year. | 34% |
| 2 years. | 31% |
| 3 years. | 27% |
Recovery after stroke.
While a lot of people die from hemorrhagic stroke, recovery for survivors is usually a slow process that often takes months or years, depending on the amount of brain tissue damage. With a good and intensive rehabilitation plan, lost functions are regained but only about 10% of survivors go on to full recovery while the majority are left with some level of physical impairment. (source)
How long the rehabilitation takes is determined by the severity of the stroke. At 6 months post-stroke, only about 20% of the survivors become functionally independent. (source)
Prevention.
Having had a first-time stroke puts you at even greater risk of having a subsequent one(s). High blood pressure is understood to be the major risk factor in hemorrhagic strokes so getting your BP under control and keeping it within safe ranges is key to preventing stroke.
Lifestyle changes like eating healthy diets, exercising, and keeping a healthy body weight are also very important, and at times surgery can be considered for prevention. (source)
Where considered necessary, surgery could be one of the preventive measures in treating an arteriovenous malformation or aneurysm that puts you at a high risk of hemorrhagic stroke. A minimally invasive surgery should be preferable in this sense.



























































































































Thanks for your blog, nice to read. Do not stop.
Thanks so much for the encouragement, friend. So glad to hear from you. I’m still very much into clinical practice and I consult in several health facilities. So sometimes I get so busy with patients that I struggle to find time to write. However, I’m passionate about writing and never going to stop.
I like the efforts you have put in this, regards for all the great articles.
Would love to always get updated on this outstanding site! .
Perfect work you have done, this site is really cool with good info .